col.c代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| #include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
unsigned long hashcode = 0x21DD09EC;
unsigned long check_password(const char* p){
int* ip = (int*)p;
int i;
int res=0;
for(i=0; i<5; i++){
res += ip[i];
}
return res;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
if(argc<2){
printf("usage : %s [passcode]\n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
if(strlen(argv[1]) != 20){
printf("passcode length should be 20 bytes\n");
return 0;
}
if(hashcode == check_password( argv[1] )){
system("/bin/cat flag");
return 0;
}
else
printf("wrong passcode.\n");
return 0;
}
|
观察代码,可知代码逻辑过程是:
1.先输入一个不少于20字节长度的值
2.对输入的前五位整数求和(int类型,一个int等于4字节,5位int类型,恰好20字节)
3.求得的和与0x21DD09EC比较,若相等则通过
重点1:
这里将输入的char类型的指针强制转换为了int指针,从而ip指针一次能够指向4个字节大小的内存区域。画个图模拟一下内存布局:
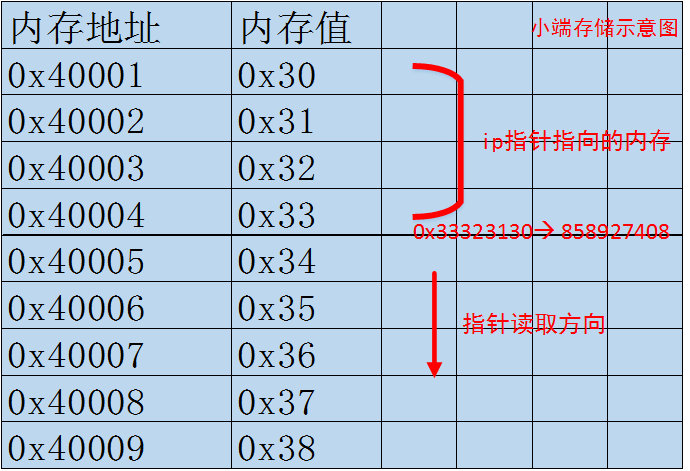
思路1:将0x21DD09EC除以5变为4字节为一组,分别输入,最后以4字节为一组进行求和即可。
比如:
1
2
3
4
| >>> 0x21DD09EC/5
113626824
>>> hex(0x21DD09EC/5)
'0x6c5cec8'
|
哦,稍等。好像不能被5整除哦。换个方式:4 x 0x01010101 + 0x1dd905e8
1
2
3
| >>> hex(0x21DD09EC-4*0x01010101)
'0x1dd905e8'
>>>
|
接下我们把刚刚的值输入:
1
2
3
4
| col@ubuntu:~$ ./col `python -c "print 16*'\x01'+'\xe8\x05\xd9\x1d'"`
daddy! I just managed to create a hash collision :)
col@ubuntu:~$
|
YES,GET FLAG!
